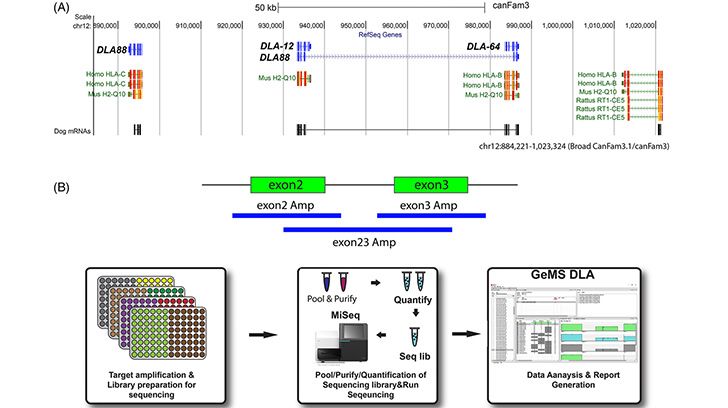
Dogs have served as one of the most reliable preclinical models for a variety of diseases and treatments, including stem/progenitor cell transplantation. At the genetic epicenter of dog transplantation models, polymorphic major histocompatibility complex (MHC) genes are most impactful on transplantation success. Among the canine class I and class II genes, DLA-88 has been best studied in transplantation matching and outcomes, with 129 DLA-88 alleles identified. In this study we developed and tested a next generation (NGS) sequencing protocol for rapid identification of DLA-88 genotypes in dogs and compared the workflow and data generated with an established DLA-88 Sanger sequencing protocol that has been in common prior use for clinical studies. By testing the NGS protocol on a random population of 382 dogs, it was possible to demonstrate superior efficacy based on laboratory execution and overall cost. In addition, NGS proved far more effective at discovering new alleles and detecting multiple alleles associated with gene duplication. A total of 51 new DLA-88 alleles are reported here. This rate of new allele discovery indicates that a large pool of yet un-discovered DLA-88 alleles exists in the domestic dog population. In addition, more than 46% of dogs carried three or more copies of DLA-88, further emphasizing the need for more sensitive and cost-effective DLA typing methodology for the dog clinical model.
Canine studies were performed with the assistance of the Canine Core at the Fred Hutchinson Center of Excellence in Hematology U54 DK106829.
