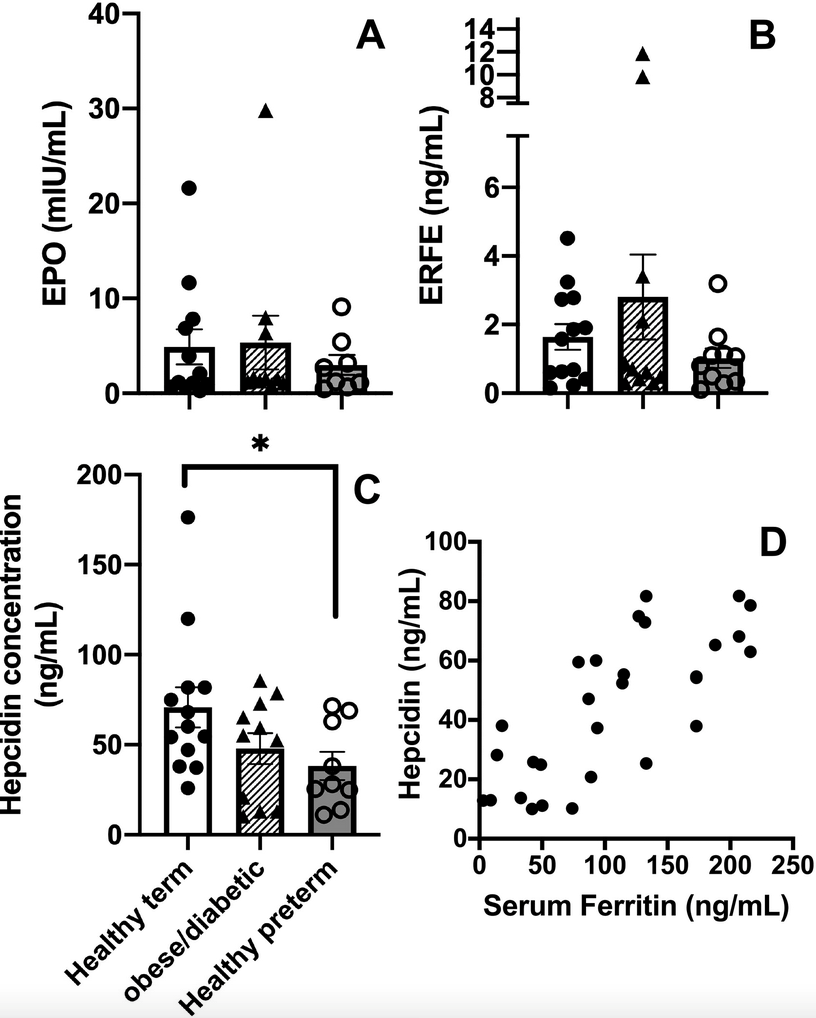
In a two-part process, we assessed elements of the principal hormonal pathway regulating iron homeostasis in human neonates. Part 1: Quantifying erythropoietin (Epo), erythroferrone (ERFE), hepcidin, and relevant serum and erythrocytic iron-related metrics in umbilical cord blood from term (n = 13) and preterm (n = 10) neonates, and from neonates born to mothers with diabetes and obesity (n = 13); Part 2: Quantifying serum Epo, ERFE, and hepcidin before and following darbepoetin administration. Part 1: We measured Epo, ERFE and hepcidin in all cord blood samples. Epo and ERFE levels did not differ between the three groups. Preterm neonates had the lowest hepcidin levels, while neonates born to diabetic women with a very high BMI had the lowest ferritin and RET-He levels. Part 2: Following darbepoetin dosing, ERFE levels generally increased (p < 0.05) and hepcidin levels generally fell (p < 0.05). Our observations suggest that the Epo/ERFE/hepcidin axis is intact in the newborn period.
Keywords: Erythroferrone; Erythropoietin; Hepcidin; Iron; RET-He; Supplementation.
This project was partially funded by University of Utah School of Medicine CIHD Pilot and Feasability NIDDK U54 Funding.